5 Ways to Block Websites on Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari
In today's hyperconnected world, staying focused can feel impossible with distracting websites just a click away. Whether you're looking to boost productivity, protect children from inappropriate content, or maintain a distraction-free work environment, knowing how to block websites in various browsers is an essential digital skill.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through 5 effective methods to block websites in popular browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari. We'll explore these solutions from the easiest to implement to the most technical, helping you choose the right approach for your specific needs.
Why Block Websites in Browsers?
Before diving into the methods, let's understand why you might want to block certain websites:
- Boost Productivity and Focus: Eliminate distracting social media sites and create a productive work environment
- Protect Children: Prevent access to inappropriate or harmful content
- Improve Security: Block access to potentially malicious websites
- Enforce Company Policies: Ensure employees aren't accessing non-work-related websites during work hours
Studies show that the average person spends 2.5 hours per day on social media alone. Blocking distracting websites can help reclaim this time for more productive activities.
Method 1: Using Browser Extensions (Recommended)
Applies to: All browsers
The simplest and most flexible way to block websites is using a dedicated extension.
Our recommended solution is the Intentional Chrome extension, which offers powerful website blocking features with an intuitive interface.
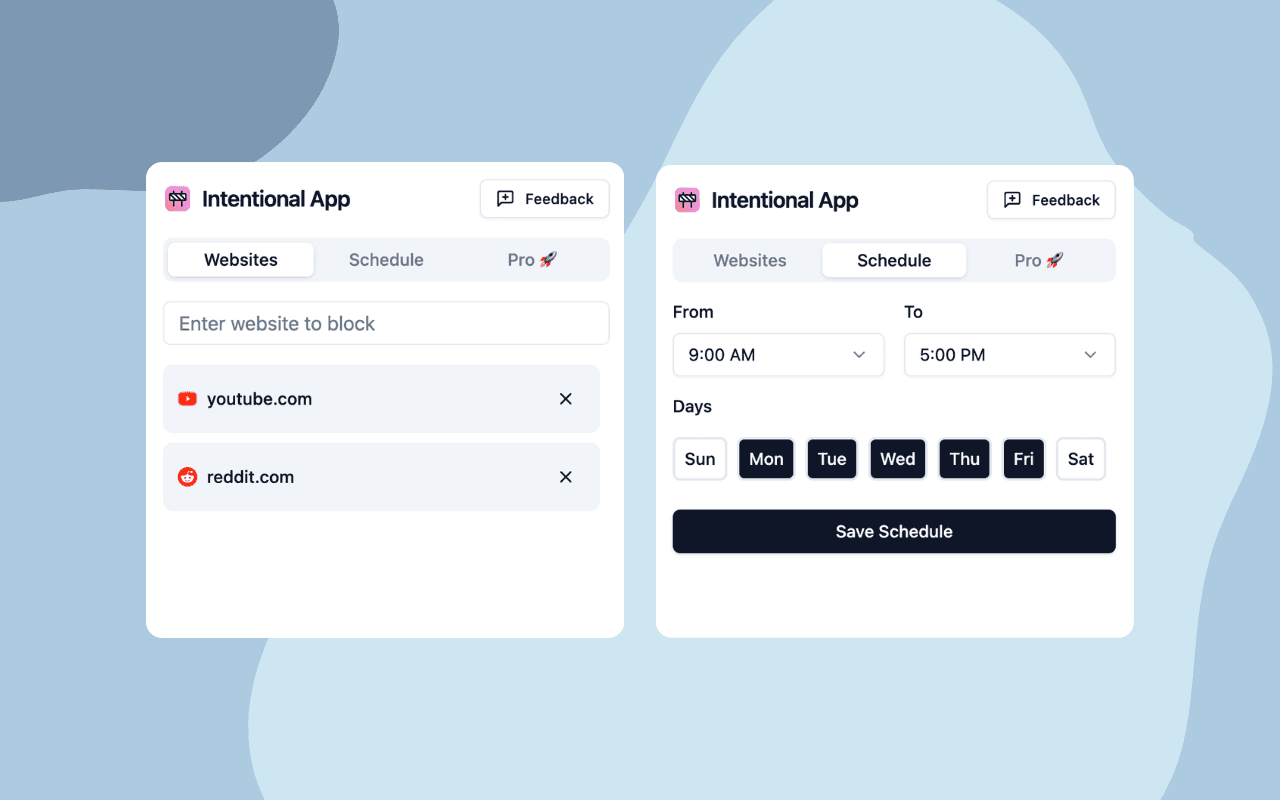
How Intentional Works?
- Select websites to block
- Add blocking schedule (or more schedules)
- Enjoy distraction-free browsing and increased productivity
Why Intentional?
Created by a software engineer who struggled with digital distractions while building a startup. After trying every available solution and finding them lacking, Intentional was born.
Our app is similar to Cold Turkey, Freedom, or StayFocusd, but it combines simplicity with powerful customization. More effective than basic ad blockers or YouTube distraction removers like DF Tube (Distraction Free for YouTube™), Unhook, or Social Focus App.
Where to download Intentional?
Pros:
- Easy to install and configure
- Flexible scheduling options
- Works across multiple browsers
- Customizable blocking messages
- Ability to allow specific pages within blocked domains
- Syncs across devices when signed in
Cons:
- Can be bypassed by switching browsers
- Requires installation on each browser

Method 2: Google Workspace Controls
Applies to: Chrome (on managed devices)
For organizations using Google Workspace, administrators can implement website blocking at the organizational level.
- Access the Google Admin console
- Navigate to Devices > Chrome > Settings
- Select your organizational unit
- Configure URL blocking rules
- Add up to 1,000 URLs to block
Detailed Implementation:
According to Google's documentation, administrators can implement URL blocking in several ways:
- URL Blocklist: Enter specific URLs to block
- URL Blocklist Exception: Allow specific exceptions to blocked URLs
- Block access to a URL: Prevent access to specific URLs
- Allow access to a URL: Explicitly allow access to certain URLs
You can also configure whether to block entire domains or just specific pages, and set custom messages that appear when users attempt to access blocked content.
Pros:
- Centralized management for organizations
- Cannot be easily bypassed by users
- Works across all managed devices
- Detailed control over exactly what's blocked
- Customizable blocking messages
- Comprehensive reporting
Cons:
- Requires Google Workspace subscription
- Only works on managed devices within the organization
- Requires administrator privileges
- May not block mobile apps outside of the browser
- More complex to set up than browser extensions
Method 3: Implementing Parental Controls
Applies to: Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari (varies by platform)
For family protection, you can use Google Family Link or system-level controls. These methods can be applied across various browsers.
Google Family Link Setup:
- Download Google Family Link on both parent and child devices
- Create a Google Account for your child
- Link the accounts
- Set website restrictions through the Family Link app
System-Level Controls:
Windows:
- Use Microsoft Family Safety
- Configure Windows Parental Controls through Settings > Family & other users
macOS:
- Open System Settings
- Navigate to Screen Time
- Navigate to Restrictions - Content & Privacy
- Click on App Store, Media, Web & Games
- Safari - Access to Web Content
- You can add only allowed websites here or click on Limit Adult Websites
Pros:
- Works across multiple browsers
- Difficult for children to bypass
- Often includes additional features like screen time limits
- Can be managed remotely (for Family Link)
- Integrates with existing operating system features
Cons:
- Less granular control than dedicated extensions
- May block more than intended with broad categories
- Setup can be complex for non-technical users
- May require subscription for advanced features
- Limited to specific user accounts
Method 4: Editing the Hosts File
Applies to: All browsers on the system
For technical users, modifying the hosts file provides system-wide website blocking across all browsers and applications.
Windows Instructions:
- Open Notepad as Administrator (right-click on Notepad and select "Run as administrator")
- Navigate to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
- Add entries like:
127.0.0.1 website.com(one domain per line) - To block subdomains as well, add:
127.0.0.1 www.website.com - Save the file
macOS Instructions:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Add: 127.0.0.1 website.com
Press Ctrl+O to save, then Ctrl+X to exit
Linux Instructions:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Add: 127.0.0.1 website.com
Press Ctrl+O to save, then Ctrl+X to exit
How It Works:
The hosts file maps domain names to IP addresses. By pointing problematic domains to 127.0.0.1 (your local computer), any requests to these websites are redirected to your own device instead of the actual website, effectively blocking access.
The hosts file method requires technical knowledge and administrator privileges, but it's highly effective and works across all browsers.
Pros:
- Works across all browsers and applications
- No software installation required
- Cannot be easily bypassed without administrator access
- System-wide blocking
- No performance impact on browsing
- Free and doesn't require third-party tools
Cons:
- Requires administrator privileges
- Technical knowledge required
- No scheduling options
- Must be manually updated
- Doesn't work for IP-based websites
- Doesn't show a blocking message (page simply won't load)
Method 5: Router-Level Website Blocking
Applies to: All devices on the network, regardless of browser
Block websites across your entire network, affecting all devices connected to your home or office internet.
- Access your router's admin panel (typically by entering 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 in your browser)
- Find Website Filtering or Parental Controls (location varies by router manufacturer)
- Add websites to block
- Apply the settings
Implementation Details:
Different routers have different interfaces, but most modern routers offer website blocking functionality. Common locations for these settings include:
- Security > Access Control
- Parental Controls
- Website Filter
- Access Restrictions
Some advanced routers even allow scheduling, so you can block certain websites during specific hours.
Pros:
- Works across all devices on the network
- Cannot be bypassed without router access
- Single point of control for all network devices
- Network-wide protection
- Blocks websites regardless of the browser or application used
- No need to install software on individual devices
Cons:
- Requires router admin access
- Interface varies by router manufacturer
- May be complex to configure
- Doesn't work when devices are off the network (e.g., using mobile data)
- Limited customization options on basic routers
- May affect all users on the network, not just specific users
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Website Blocking Method
Each of the five methods described offers unique advantages and limitations. The best choice depends on your specific needs:
-
For Individual Users: Browser extensions like Intentional offer the best balance of simplicity and functionality, with customizable scheduling and easy setup.
-
For Parents: Consider combining parental controls (Method 3) with router-level blocking (Method 5) for comprehensive protection across all devices.
-
For Organizations: Google Workspace controls (Method 2) provide centralized management, while router-level blocking ensures network-wide compliance.
-
For Technical Users: The hosts file method (Method 4) offers a no-cost, system-wide solution without additional software.
Remember that digital well-being is about more than just blocking websites—it's about developing healthy digital habits. Website blocking tools should be part of a broader strategy that includes mindful technology use, regular digital detoxes, and clear boundaries between work and personal time.
Enhance Your Productivity with Our Chrome Extension
Download our Chrome extension to block distractions and stay focused. Experience seamless productivity with just a click.